Difference Between OS1 and OS2 Fiber Optic Cable
OS1 and OS2 are two specifications for single mode fiber optic cabling. The differences between OS1 and OS2 fiber optic cables mainly lie in the performance due to cable construction. Only when you figure out the differences between them can you improve the functionality of the optical device. Here is some information related to the differences between OS1 and OS2 fiber optic cable.
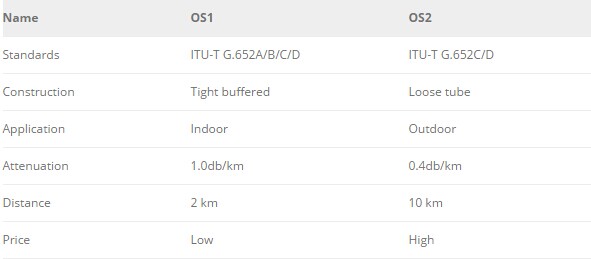
OS1 and OS2 are cabled optical fiber specifications. Category OS1 is appropriate to internal tight buffered cable construction, while Category OS2 is appropriate to a loose tube or blown fiber solution (where the cabling process applies no stress to the optical fibers). The loose tube cable is made from optical fiber and gives the best installed performance of 0.4db per km.
OS1 single mode fiber is a broader concept than OS2 single mode fiber, because it is compliant with specifications of ITU-T G.652 (including ITU-T G.652A, ITU-T G.652B, ITU-T G.652C and ITU-T G.652D). However, OS2 single mode fiber is only compliant with ITU-T G.652C or ITU-T G.652D standards.
OS1 and OS2 have different degrees of attenuation. OS1 has more than two times loss than OS2. In general, the maximum attenuation for OS1 is 1.0 db/km and 0.4db/km for OS2. As a result, the maximum transmission distance of OS1 single mode fiber is 2 km but the maximum transmission distance of OS2 single mode fiber can reach 5 km and up to 10 km. Though the maximum transmission distance of OS2 single mode fiber is much longer than that of OS1, OS1 is much cheaper than OS2 for the cheaper materials.
Since ITU-T G.652A or ITU-T G.652B optical fibers are not intended to be used for transmission at 1383nm wavelength due to their inherent attenuation characteristics. The attenuation at water peak region of the spectrum is quite high and are not recommended for use. But ITU-T G.652C and ITU-T G.652D optical fibers can be used for a full spectrum transmission with lower attenuation values at 1383nm, which means that OS2 fiber optic cable can operate at a wider range of wavelengths than OS1 fiber optic cable.
OS1 fiber optic cable is designed for use in internal situations where the maximum distance is 2000 meters, such as in a campus or data center. For indoor applications, the jacketed fiber is generally enclosed, with a bundle of flexible fibrous polymer strength members like aramid in a lightweight plastic cover to form a simple cable. By contrast, OS2 fiber optic cable is normally used outdoors and designed for maximum distance of 5,000 to 10,000 meters. Any type of indoor fiber is more tolerant of bending, because the fiber is mostly plastic and has the ability to bend. The buffered cable can reduce the risk of catastrophic damage. Most outdoor fibers are sensitive to bend. Thus they are more likely to break during installation. Both OS1 and OS2 single mode fibers allow speeds of 1 to 10 Gigabit Ethernet.
One thing you need to pay attention to is that OS2 fiber optic cable can not be connected with OS1 fiber optic cable because it may lead to unpredictable signal performance. OS1 and OS2 specifications are not only applied to fiber optic cables, but also single mode fiber optic patch cables. Whether to choose OS1 or OS2 specification depends on your requirements in real situations. Consider all the above-mentioned factors and you'll find the most proper one.