What's the Difference Between Direct Uplink and Fan-Out Uplink?
Fan-out cable, also called breakout cable is referred to be one of the latest enabling technologies to increase port densities and reduce the costs. Taking one (large bandwidth) physical interface and breaking it out into several (smaller bandwidth) interfaces, it has been highly recommended to be used in network migration. In this post, I will compare the 40G direct uplink and the fan-out 4x10G uplink configurations and their inherent differences in maximum server scalability.
For a leaf/spine network architecture, the number of connections used for uplinks from each leaf switch determines the total number of spine switches in the design. Meanwhile, the number of ports on each spine switch determines the total number of leaf switches.
Now, imagine that we’re building a network that supports 1200 10G servers in one fabric with 2.5:1 oversubscription. The network must seamlessly expand to over 5000 10G servers without increasing latency or oversubscription in the future. Next, I will compare two different approaches.
The following picture shows us a 40G fabric to us. Each of the spine switches has 32 ports of 40G. Each leaf ToR (Top of Rack) switch is connected to the spine with 4 ports of 40G using the leaf switches 40G QSFP uplink ports. There will be 40 servers per rack connected to each leaf switch. Namely, it allows a maximum is 1280 x 10G servers at 2.5:1 oversubscription. This meets the initial scale target of 1200 servers however, it cannot scale larger. Before the network can achieve the 5000 server design goal, the 40G design will have to be re-architected.
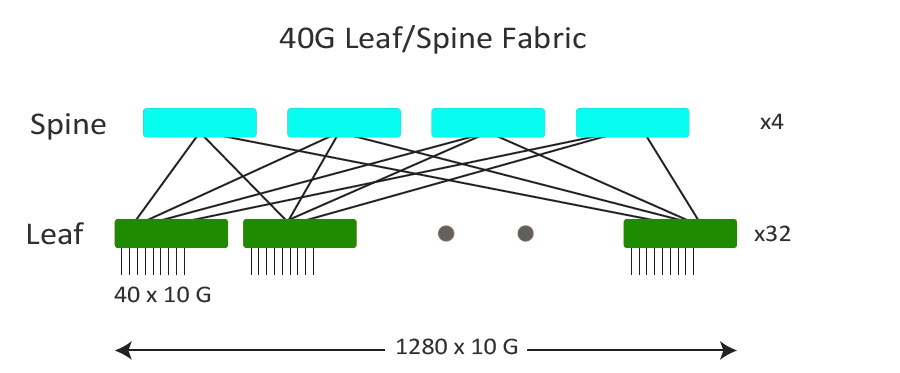
As mentioned above, a direct 40G uplink is not an ideal configuration for a cost-effective server scalability. So, what level of server scalability can be achieved when using fan-out the leaf switch uplink ports with 4 x 10 G each?
The picture below shows a 10G leaf/spine fabric to us. With a QSFP+ to SFP+ optical fan-out cable, each QSFP leaf port is now fanned out to 4 x 10G interfaces each, for a total of 16 x 10G uplinks. Each of the spine switches now has 128 ports of 10G. Each leaf switch is connected to the spine with 16 ports of 10G. In this case, the maximum scale is 5120 x 10G servers at 2.5:1 oversubscription. Obviously, with the same bandwidth, latency and oversubscription, this fabric is better. It can not only be built to 1200 servers for present demand but also can seamlessly scale to over 5000 servers in the future.
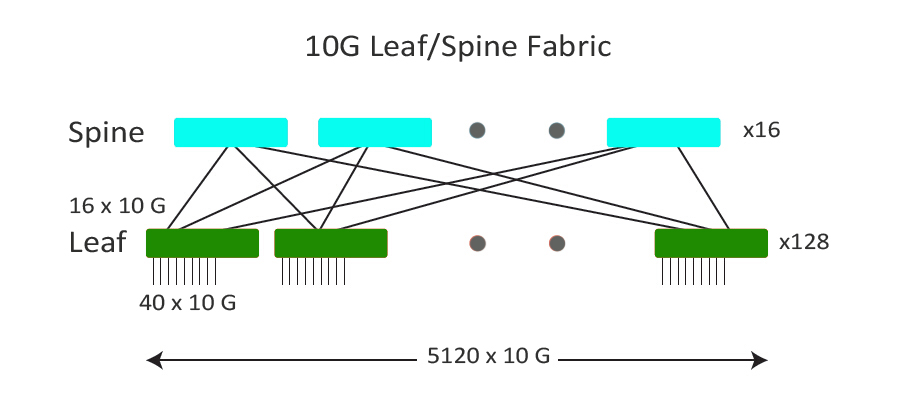
Through the above analysis, we can see that the 10G leaf/spine fabric design offers four times greater scalability than the 40G fabric design when they have the same hardware, bandwidth, latency and oversubscription. These two configuration scenarios show us how fan-out technology are used to scale up a data center fabric. As the 10G network is widely deployed in today’s data center, the 10G direct attach cables (like Cisco SFP-H10GB-ACU10M) are preferred by many designers and companies. But higher speed demand such 40/100G is also needed. The fan-out technology not only enables new levels of server scalability, but also promotes a time-saving and cost-effective network migration.
