How to Choose Fiber Optic Cables?
Choosing the right type of fiber optic cable is very important for the proper operation of the networks. Without fiber optic cables, the system may be slow and may not operate at optimal conditions. If you’re seeking to expand your business, you should select products that will ensure that your business operates optimally. Bandwidth requirements, transmission distances, applications, and network architecture influence fiber selection just as much as current needs. Here are some tips on how to select the proper fiber optic cables.
When a company is investigating an upgrade to a fiber-optic network, one of the most basic questions to answer is "which kind of fiber do I need to use?" Generally speaking, there are two main kinds of fiber-optic cabling: single-mode and multimode.
Single-mode fiber optic cable has a small diametral core that allows only one mode of light to propagate. Because of this, the number of light reflections created as the light passes through the core decreases, lowering attenuation and creating the ability for the signal to travel faster, further. This application is typically used in long distance, higher bandwidth runs by Telcos, CATV companies, and colleges and universities.
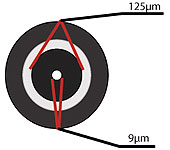
Multimode fiber opticcable has a large diametral core that allows multiple modes of light to propagate. Because of this, the number of light reflections created as the light passes through the core increases, creating the ability for more data to pass through at a given time. Because of the high dispersion and attenuation rate with this type of fiber, the quality of the signal is reduced over long distances. This application is typically used for short distance, data and audio/video applications in LANs. RF broadband signals, such as what cable companies commonly use, cannot be transmitted over multimode fiber.
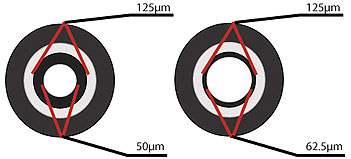
Although multimode distance capability is growing, it can't compete with the distances single-mode fiber can accommodate. In addition to its far reach, single-mode fiber offers virtually unlimited bandwidth, making it an excellent solution for campus and metropolitan networks. The power of single-mode fiber comes from the high-powered lasers that transmit data at greater distances than the light used with multimode fiber. While single-mode fiber costs about the same as multimode, it's often reserved for backbone connections that don't have the higher-cost network interfaces associated with single-mode fiber.
Every designer should make an assessment of how they will use fiber optic cables in their applications. These assessments can improve your existing design significantly. Once you evaluate the needs of a network, you can establish what’s needed. If you will be connecting a fiber optic cable to a surveillance camera, the type of cable will be different than connecting it to an existing foundation. The number of connections to multiple service applications will affect the fiber strand count. That’s why you need to know your applications clearly before you choose the appropriate type of fiber cables.
Environmental conditions are other factors that must be evaluated when selecting protective fiber jackets. For example, PVC cable jackets are suitable for indoor environments; however, cabling that runs through a plenum space will need to conform to fire codes. In these cases, plenum cable jackets are required. Similarly, OSP jackets are used for outdoor applications, but when the cable needs to enter a building beyond 50 ft, installers must transition to an indoor-rated cable in conformance with fire codes. One way to eliminate this transition point is to use a cable jacket with an indoor/outdoor rating. These indoor/outdoor cables are available with either a PVC or plenum rating.
Before choosing which kind of fiber optic cable should be used, you need to know the applications. Multimode fiber can allow transmission distances of up to 300-400 meters and the use of relatively inexpensive fiber optic transmitters and receivers. There will be bandwidth limitations of a few hundred MHz per Km of length. Consequently, a 10 mile link will be limited to about 10 to 30 MHz. Single-mode can get you 10km, 40km, 80km, and even farther – you just need to use the appropriate optic for the distance required. Prices go up accordingly. As one the main fiber optical manufacturers in China, Fiberstore (FS.COM) offers various kind of fiber optic cables, like single mode fiber patch cables, multimode fiber patch cables, MTP/MPO fiber cables and so on. All these cables can be customized to meet your special requirements.